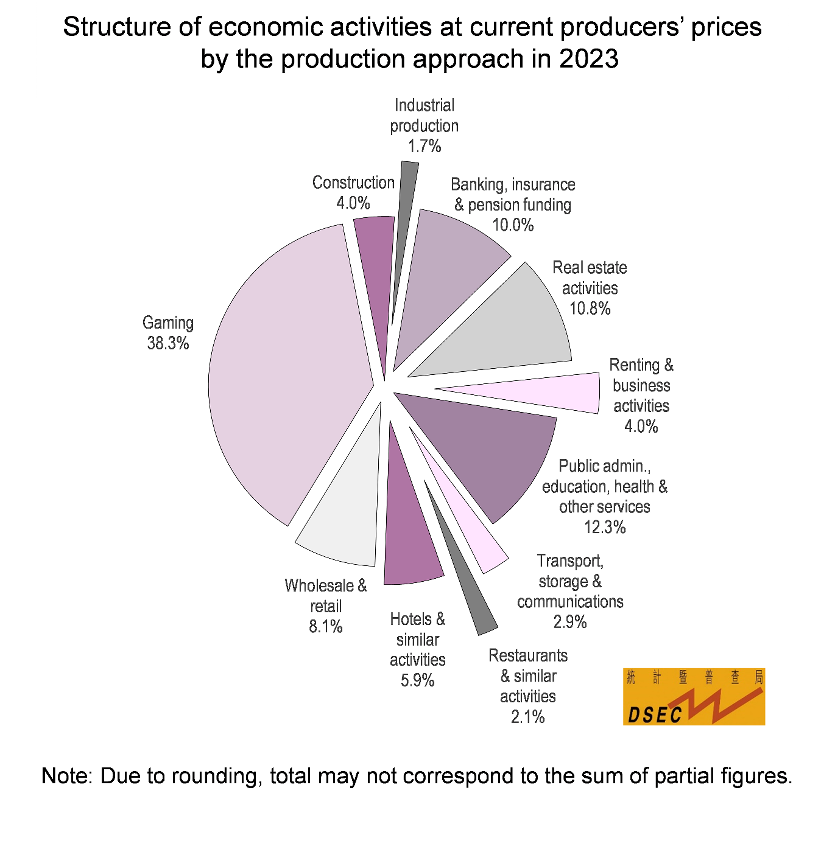
 Structure of economic activities at current producers’ prices by the production approach in 2023
Structure of economic activities at current producers’ prices by the production approach in 2023
Non-gaming industries in Macao accounted for over 60% of the total Gross Value Added in 2023
Information from the Statistics and Census Service (DSEC) indicated that Gross Value Added of the tertiary sector in Macao (i.e. service sector, such as wholesale & retail trade, restaurants & similar activities, financial activities and gaming) surged by 76.4% year-on-year in real terms in 2023, driven by an upsurge (+395%) in the number of visitor arrivals. Its relative importance in the industrial structure grew by 3.6 percentage points to 94.4%. Gross Value Added of the secondary sector (e.g. industrial production, manufacturing and construction) rose by 6.8% in real terms, while its relative importance in the industrial structure dropped by 3.6 percentage points to 5.6%. Analysed by economic activity, Gross Value Added of non-gaming industries increased by 20.7% year-on-year in real terms to MOP220.7 billion, which accounted for 61.7% of the total Gross Value Added, up by 12.9 percentage points compared to 2019.
Gross Value Added of the tertiary sector showed a real growth of 76% year-on-year, with its relative importance increasing to 95%
Gross Value Added of all economic activities expanded by 70.0% year-on-year in real terms, underpinned by the resumption of local economic activities. Gross Value Added of the tertiary sector soared by 76.4% in real terms on account of the revival of tourism activity, with Gross Value Added of most of the economic activities recording year-on-year growth. Notable rise was observed in the Gross Value Added of tourism-related industries such as Gaming (+354.8%), Restaurants & Similar Activities (+112.5%), Hotels & Similar Activities (+88.1%) and Wholesale & Retail Trade (+79.4%). Meanwhile, Gross Value Added of the secondary sector increased by 6.8% in real terms, with that of the Manufacturing sector, the Electricity, Gas & Water Supply sector and the Construction sector rising by 42.7%, 8.1% and 1.6% respectively.
As regards industrial structure, the relative importance of the tertiary sector expanded by 3.6 percentage points year-on-year to 94.4% due to a relatively large growth in Gross Value Added, whereas the relative importance of the secondary sector decreased by 3.6 percentage points to 5.6%. With respect to the structure of economic activities, the share of the Gaming sector (38.3%) rebounded by 23.5 percentage points; meanwhile, the share of the non-gaming industries receded to 61.7%, which represented an increase of 12.9 percentage points when compared to 2019. The proportions of Hotels & Similar Activities (5.9%) and Restaurants & Similar Activities (2.1%), which fall under the tertiary sector, grew by 3.5 percentage points and 0.4 percentage points respectively year-on-year. On the other hand, the proportions of the Construction sector (4.0%), the Electricity, Gas & Water Supply sector (0.9%) and the Manufacturing sector (0.8%), which are in the secondary sector, decreased by 2.9 percentage points, 0.5 percentage points and 0.1 percentage point respectively.
Relative importance of taxes on production & imports and operating surplus increased
Regarding primary distribution of income (i.e. the distribution of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) among taxes on production & imports, operating surplus and compensation of employees), Taxes on Production & Imports, Operating Surplus and Compensation of Employees rose by 270.9%, 140.1% and 6.4% year-on-year to MOP80.3 billion, MOP152.9 billion and MOP125.4 billion respectively in 2023, which accounted for 22.4%, 42.6% and 35.0% of GDP. As the growth in Compensation of Employees was smaller than that in Taxes on Production & Imports and Operating Surplus, the share of Compensation of Employees showed a fall of 23.0 percentage points year-on-year; the shares of Taxes on Production & Imports and Operating Surplus, on the other hand, grew by 11.7 percentage points and 11.3 percentage points respectively.
Explanatory Note
Industrial structure
Industrial structure reflects the relative importance of different economic activities in terms of their respective value-added contribution to the economy. Value added refers to the value created in the process of production of an economic activity (e.g. a sector or an industry), i.e. the value of goods and services produced in the economic activity, less the value of goods and services consumed in the production process (e.g. operating expenses such as water and electricity charges and rents). Sectors of industries are classified as primary (e.g. fishing, agriculture and animal husbandry), secondary (e.g. industrial production, manufacturing and construction) and tertiary (i.e. service sector, such as wholesale & retail trade, restaurants & similar activities, financial activities and gaming).
Statistical discrepancy between production approach and expenditure approach
The GDP calculated based on the production approach and the expenditure approach, which reflect the results of the same production activities, should be consistent in theory. However, in practice, the results calculated using the two approaches may differ owing to various factors such as data sources, statistical coverage, calculation methods, etc. This discrepancy is known as statistical error, which is acceptable within a specific margin. In the context of Macao, the margin of statistical error is basically maintained within 3.0%.